Solutions from Zhongtian Transformers in the New Energy Sector
Time:2024-10-28 Auther:ZTelec-www.ztelectransformer.com
Transformers are devices that utilize the principle of electromagnetic induction to change AC voltage. They have a wide range of applications in the energy sector, enabling functions such as voltage conversion and transmission, efficient power transmission, system stability and reactive support, grid interconnection and hierarchical operation, isolation, and fault protection, all of which require transformers.

The importance of transformer manufacturing for the energy industry cannot be overlooked, making the choice of transformer a crucial issue. With the increasing intensity of market competition, cost-effective transformers are gaining more preference.

Transformer industrial profile
Power Transmission:
The energy industry holds a fundamental and pillar position in the national economy, significantly impacting national security, social stability, and the living standards of the people. The stable supply and efficient utilization of energy, especially in the electricity sector, are key factors in safeguarding national security, promoting social stability, and improving people’s quality of life.
As global attention to green and low-carbon development grows, electrical equipment using green energy, as key devices for energy transmission and conversion, will play an increasingly important role in the energy sector. Continuous technological advancements and ongoing policy support will further drive the development of the transformer market.
Components and Functions of Transformer Systems:
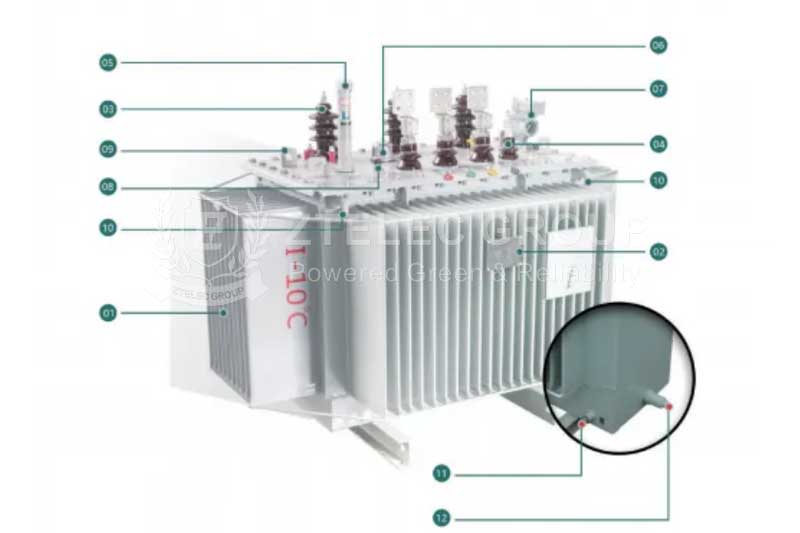
Transformer Structure Diagram
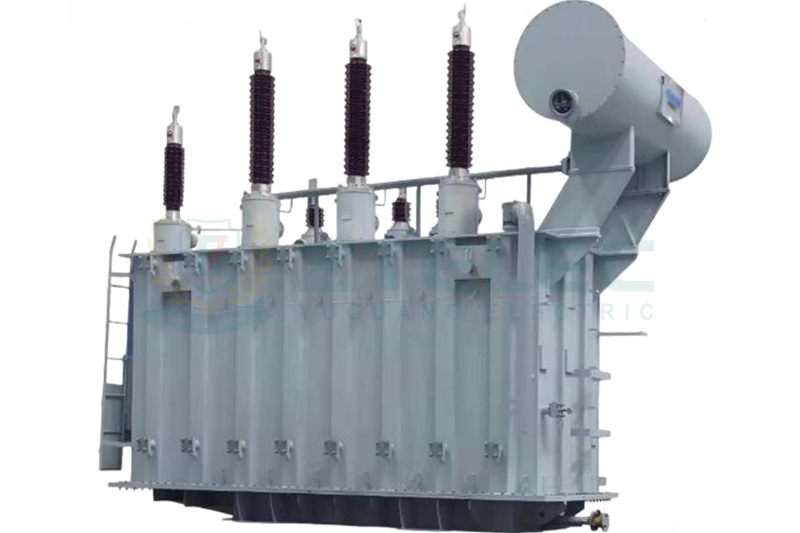
The main components of a transformer include the core, coil windings, insulating bushing, oil tank, and accessories. The core is the critical component of the transformer, responsible for guiding magnetic flux; the coil windings consist of the primary and secondary coils, which handle current transformation; the insulating bushing protects and secures the windings; the oil tank and its accessories, including the oil cushion and radiator, are used for cooling and protecting the transformer.
Function of the Transformer Oil Tank:
The oil tank of the transformer is its outer shell, containing the core, windings, and transformer oil, responsible for supporting the transformer structure and housing essential components. It also facilitates some heat dissipation. The corrugated and flat structures surrounding the oil tank are called radiators. When a temperature difference occurs in the upper oil of the transformer, a cycle is formed through the radiators, cooling the oil before it flows back to the oil tank, thus reducing the oil temperature. To enhance cooling efficiency, methods such as air cooling, forced oil-air cooling, or forced oil-water cooling can be utilized.
Function of the Transformer High and Low Voltage Bushings:
The transformer bushing is the main insulating device outside the transformer box. The lead wires of the transformer windings must pass through the insulating bushings, providing insulation between the lead wires and between the lead wires and the transformer shell, while also fixing the lead wires. Due to different voltage levels, insulating bushings come in forms such as pure porcelain bushings, oil-filled bushings, and capacitive bushings. Pure porcelain bushings are mostly used for transformers at 10kV and below; they contain a conductive copper rod running through the porcelain bushing which is air insulated. Oil-filled bushings are mainly used in 35kV transformers, where oil fills the porcelain bushing, and a conductive copper rod is inserted, insulated with paper.
Function of the Gas Relay:
Gas relays are primarily used to protect various types of oil-immersed fully sealed transformers. During operation, internal faults generate gas, which accumulates in the gas relay’s gas collection chamber. When the volume of gas reaches a certain level, it triggers an alarm or disconnects contacts, producing an alarm signal or a cut-off signal to protect the transformer.
Application of Solutions in New Energy Power Transmission
New Energy Power Generation:
Selecting transformers in the new energy sector requires consideration of several key factors, including load requirements, voltage levels, efficiency and energy consumption, cooling methods, noise control, ease of maintenance, and economic viability. Based on comprehensive research and investigation, the use of amorphous alloy oil-immersed transformers in the new energy sector proves to be a good choice.

High Efficiency and Energy Saving:
Amorphous alloys have a high magnetic permeability and extremely low losses, mainly due to their high permeance and low coercive forces. The saturation magnetic flux density of amorphous alloys is high, providing strong resistance to saturation, which allows transformers to operate under high current conditions without saturating, thereby enhancing their load capacity. The eddy current losses of amorphous alloys are significantly lower than those of cores made from cold-rolled silicon steel sheets, resulting in very low no-load losses and notable energy-saving effects.
Environmental Protection:
Amorphous alloy transformers are small and lightweight, making them easy to integrate into various power systems, reducing material usage, and aligning with energy-saving and environmental protection principles.
Low Long-Term Costs:
Due to their high efficiency and low loss characteristics, the operational costs of amorphous alloy transformers are lower compared to traditional transformers, offering better economic benefits over the long term. The longer lifespan of amorphous alloy transformers reduces maintenance and replacement frequency, further lowering operational costs.







