How does a transformer change voltage and current?
Time:2024-11-1 Auther:ZTelec-www.ztelectransformer.com
Basic principles of transformers
Transformer is a device that uses the principle of electromagnetic induction to realize power transmission. It mainly consists of core, winding, insulation material and shell. The iron core is one of the main components of the transformer. In addition to supporting and fixing the windings, the iron core can also gather magnetic field lines between the windings, thereby improving the efficiency of power transmission. The winding is the most basic electrical component in a transformer. It is composed of wires and can be used to transmit electrical energy. Insulating material is used to isolate the electric field between the winding and the casing to avoid electrical breakdown. The outer shell of the transformer mainly plays the role of protection and isolation.
The basic principle of a transformer is to use mutual inductance to achieve power transmission. When one side of a transformer is energized, an alternating magnetic field is established in its windings. Since the magnetic field lines are connected, this magnetic field will also pass through the windings of the transformer and produce a voltage. When a conductor in the winding on the other side approaches, it will be affected by the magnetic field of the transformer, thereby generating an induced electromotive force, causing current to flow. In this way, the transmission of electrical energy is achieved.
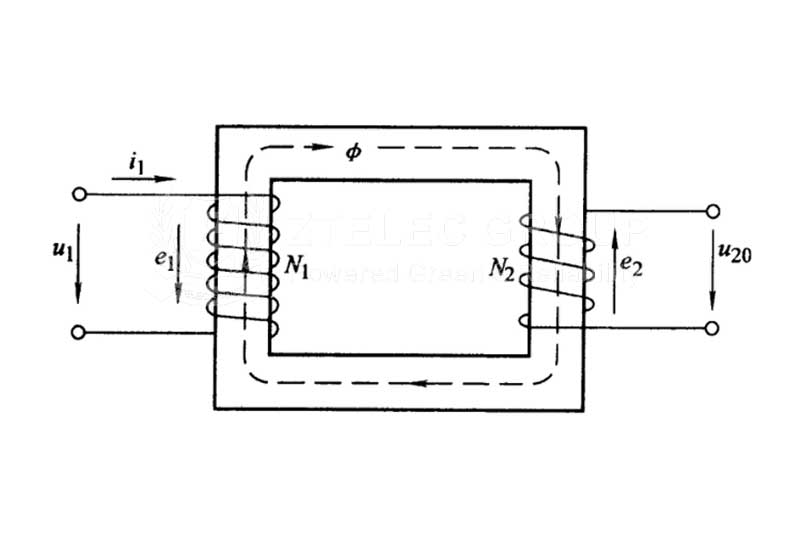
How does a transformer change voltage?
A simple single-phase transformer consists of two conductors. When one of the conductors has some unspecified current (such as alternating current or pulsed direct current) to pass through, a variable magnetic field is generated. According to the principle of mutual induction of electromagnetism, this changing magnetic field will cause a potential difference in the second conductor. If the second conductor is part of a closed circuit, then the closed circuit will produce a current. Electricity is then transmitted.
In a general-purpose transformer, the relevant conductor is a coil of (mostly copper) wire, because the magnetic field generated by the coil is much greater than that of a straight wire.
According to the principle of electromagnetic induction, the coil in the changing magnetic field will generate induced current. And the transformer has at least two coils which are called the primary side and the secondary side. The strength of the magnetic field is related to the induced current generated and the number of turns of the coil.
Regardless of the loss, the electrical power transmitted by the transformer is the same, so that the voltage generated by the secondary side will change according to the change in the number of turns of the coil, thereby changing the voltage. And the transformer is named accordingly.
Because only alternating magnetic field has electromagnetic induction phenomenon, the magnetic field generated by direct current is constant and does not change, so the transformer can only change the voltage of alternating current.

How does a transformer change current?
The process by which a transformer changes current is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction and the law of conservation of power. When the AC power supply is connected to the primary coil of the transformer, an alternating magnetic flux is generated in the core. This magnetic flux passes through the secondary coil, which induces an electromotive force in the secondary coil, and thus generates a current. Since the input power (primary power) of the transformer is equal to the output power (secondary power). In the case of ignoring the loss, when the voltage changes, the current will also change accordingly to maintain the balance of power.
Specifically, if the secondary voltage is increased, the secondary current will decrease in order to maintain the conservation of power. Conversely, if the secondary voltage is reduced, the secondary current will increase. This change in current is determined by the ratio of turns of the transformer (the ratio of turns of the primary coil and the secondary coil). The higher the turn ratio, the higher the secondary voltage and the lower the secondary current. The smaller the turn ratio, the lower the secondary voltage and the larger the secondary current.
Therefore, the transformer realizes the transmission and conversion of electrical energy by changing the proportional relationship between voltage and current.
Why can the transformer change the voltage level?
The level at which the transformer changes the voltage is determined by its working principle. There are two mutually insulated windings around the closed iron core, in which the power supply is called the primary winding, and the output electric energy is called the secondary winding. When the AC power supply is added to the primary winding, there is an AC current through the winding, creating an alternating magnetic flux in the core, which not only passes through the primary winding but also through the secondary winding. Induced electromotive force E1 and E2 are generated in the two windings respectively. At this time, if the secondary winding is connected with the external circuit load, there is current flowing into the load, that is, the secondary winding has electrical energy output. E1/E2=N1/N2, I1/I2=N21/N1, the ratio of the induction potential of the first and secondary winding of the transformer is equal to the ratio of the number of turns of the first and secondary winding, the ratio of the current of the first and secondary winding is inversely proportional to the number of turns of the first and secondary winding. The transformer is based on the principle of electromagnetic induction through the change of the number of turns of the first and secondary winding to change the voltage of the first and secondary winding.




